Sensor for Real-Time Glucose Measurement in Aqueous Media based on Nanomaterials Incorporating an Artificial Neural Network Algorithm on a System-On-Chip
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17488/RMIB.44.4.5Keywords:
ANN-MLP, multi-walled CNT, electrochemical sensor, nanostructured glucose sensor, ESP32 SoCAbstract
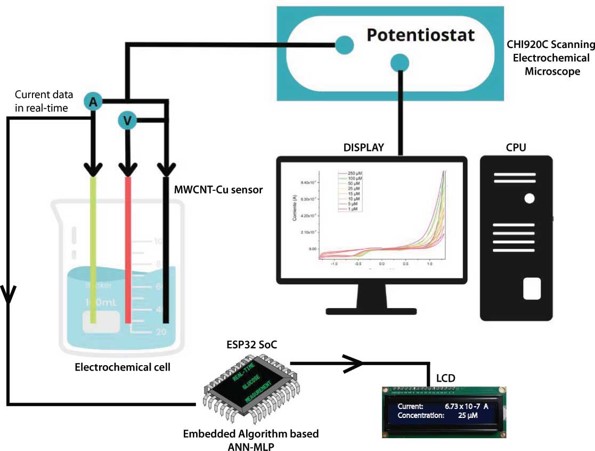
The aim of this paper is to present the development of a real-time measurement system for glucose in aqueous media. The proposed system incorporates two lines of research: i) design, synthesis, and implementation of a non-enzymatic electrochemical sensor of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes with Copper nanoparticles (MWCNT-Cu) and ii) design and implementation of a machine learning algorithm based on an Artificial Neural Network Multilayer Perceptron (ANN-MLP), which is embedded in an ESP32 SoC (System on Chip). From the current data that is extracted in real-time during the oxidation-reduction process to which an aqueous medium is subjected, it feeds the algorithm embedded in the ESP32 SoC to estimate the glucose value. The experimental results show that the nanostructured sensor improves the resolution in the amperometric response by identifying an ideal place for data collection. For its part, the incorporation of the algorithm based on an ANN embedded in a SoC provides a level of 97.8 % accuracy in the measurements. It is concluded that incorporating machine learning algorithms embedded in low-cost SoC in complex experimental processes improves data manipulation, increases the reliability of results, and adds portability.
Downloads
References
R. Wilson and A. P. F. Turner, “Glucose oxidase: an ideal enzyme,” Biosens. Bioelectron., vol. 7, no. 3, pp. 165–185, Jan. 1992, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/0956-5663(92)87013-F
P. N. Bartlett and F. A. Al‐Lolage, “There is no evidence to support literature claims of direct electron transfer (DET) for native glucose oxidase (GOx) at carbon nanotubes or graphene,” J. Electroanal. Chem., vol. 819, pp. 26–37, Jun. 2018, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2017.06.021
P. Bollella and L. Gorton, “Enzyme based amperometric biosensors,” Curr. Opin. Electrochem., vol. 10, pp. 157–173, Aug. 2018, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coelec.2018.06.003
G. Wang, X. He, L. Wang, A. Gu, Y. Huang, B. Fang, B. Geng, X. Zhang, “Non-enzymatic Electrochemical Sensing of Glucose,” Microchim. Acta, vol. 180, pp. 161–186, Feb. 2013, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-012-0923-1
D.-W. Hwang, S. Lee, M. Seo, and T. D. Chung. “Recent Advances in Electrochemical Non-enzymatic Glucose Sensors - A Review,” Anal. Chim. Acta, vol. 1033, pp. 1–34, Nov. 2018, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2018.05.051
X. Kang, Z. Mai, X. Zou, P. Cai, and J. Mo. “A sensitive nonenzymatic glucose sensor in alkaline media with a copper nanocluster/multiwall carbon nanotube-modified glassy carbon electrode,” Anal. Biochem., vol. 363, no. 1, pp. 143-150, Apr. 2007, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2007.01.003
A. B. Radwan, S. Paramparambath, J.-J. Cabibihan, A. K. Al-Ali, P. Kasak, et al., “Superior Non-Invasive Glucose Sensor using Bimetallic CuNi nanospecies coated mesoporous carbon,” Biosensors, vol. 11, no. 11, art. no. 463, Nov. 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11110463
C. Tiwari, S. S. Jha, R. Kumar, M. Chhabra, B. D. Malhotra, and A. Dixit, “Exfoliated graphite carbon paper-based flexible nonenzymatic glucose sensor,” Mater Sci. Eng. B, vol. 285, art. no. 115931, Nov. 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2022.115931
Q. Fang, H. Wang, X. Wei, Y. Tang, et al., “Cu Aerogels with Sustainable Cu(I)/Cu(II) Redox Cycles for Sensitive Nonenzymatic Glucose Sensing,” Adv. Healthc. Mater., Jun. 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/adhm.202301073
Y. Zhao, Y. Jiang, Y. Mo, Y. Zhai, J. Liu, A. C. Strzelecki, X. Guo, C. Shan, “Boosting electrochemical catalysis and nonenzymatic sensing toward glucose by Single‐Atom PT supported on Cu@CuO Core–Shell nanowires,” Small, vol. 19, no. 18, art. no. 2207240, Jan. 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202207240
A. Osorio Villa, “Oxidación electroquímica de glucosa con nanopartículas de oro soportadas en pasta de grafito/carbon (AuNPs/C),” M.S. tesis, CIDETEQ, Tijuana, México, 2017. [Online]. Available: http://cideteq.repositorioinstitucional.mx/jspui/handle/1021/163
L. N. T. Mai, T. H. Tran, Q.-B. Bui, and H.-T. Nhac-Vu, “A novel nanohybrid of gold nanoparticles anchored copper sulfide nanosheets as sensitive sensor for nonenzymatic glucose detection,” Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp., vol. 582, art. no. 123936, Dec. 2019, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2019.123936
T. T. Aun, N. M. Salleh, U. F. M. Ali, and N. S. A. Manan, “Non-Enzymatic glucose sensors involving Copper: An Electrochemical perspective,” Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem., vol. 53, no. 3, pp. 537–593, Sep. 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/10408347.2021.1967720
G. Martínez-Saucedo, M. Ugalde-Reygadas, J.J. Alcántar Peña, G. Lastra-Medina, J. Márquez-Marín, G. Torres-Delgado, R. Castanedo-Pérez, I.R. Chávez-Urbiola, “Non-enzymatic glucose sensor using nanostructured copper oxide thin films deposited by spray pyrolysis,” Surf. Interfaces, vol. 37, art. no. 102702, Apr. 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2023.102702
O. Ghodbane, L.Roué, and D. Bélanger, “Copper electrodeposition on pyrolytic graphite electrodes:Effect of the copper salt on the_electrodeposition_process,” Electrochim. Acta, vol. 52, no. 19, pp. 5843–5855, May 2007, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2007.03.009
X. Zhang, G. Wang, X. Liu, J. Wu, M. Li, J. Gu, H. Liu, and B. Fang, “Different CUO nanostructures: synthesis, characterization, and applications for glucose sensors,” J. Phys. Chem. C, vol. 112, no. 43, pp. 16845–16849, Oct. 2008, doi: https://doi.org/10.1021/jp806985k
J. Yang, W.-D. Zhang, and S. Gunasekaran, “An amperometric non-enzymatic glucose sensor by electrodepositing copper nanocubes onto vertically well-aligned multi-walled carbon_nanotube_arrays,” Biosens. Bioelectron, vol. 26, no. 1, pp. 279–284, Sep. 2010, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2010.06.014
A. Singh, A. Sharma, A. Ahmed, A. K. Sundramoorthy, H. Furukawa, S. Arya and A. Khosla, “Recent advances in Electrochemical biosensors: applications, challenges, and future scope,” Biosensors, vol. 11, no. 9, art. no. 336, Sep. 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11090336
Y. Zhao, H. Zhang, Y. Li, X. Yu, et al., “AI powered electrochemical multi-component detection of insulin and glucose in serum,” Biosens. Bioelectron., vol. 186, art. no. 113291, Aug. 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2021.113291
A. C. de Sá, A. Cipri, A. González-Calabuig, N. R. Stradiotto, and M. del Valle, “Resolution of galactose, glucose, xylose and mannose in sugarcane bagasse employing a voltammetric electronic tongue formed by metals oxy-hydroxide/MWCNT_modified_electrodes,” Sens. Actuators B Chem., vol. 222, pp. 645–653, Jan._2016, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2015.08.088
M.-L. Chen and W.-C. Oh, “Synthesis and highly visible-induced photocatalytic activity of CNT-CdSe composite for methylene blue solution,” Nanoscale Res. Lett., vol. 6, art. no. 398, May 2011, doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/1556-276x-6-398
N. Torto, T. Ruzgas, and L. Gorton, “Electrochemical oxidation of mono- and disaccharides at fresh as well as oxidized copper electrodes in alkaline media,” J. Electroanal. Chem., vol 464 no. 2, Mar. 1999, pp. 252-258, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-0728(99)00041-8
A. M. Gonzalez-Zapata, L. G. de la Fraga, B. Ovilla-Martinez, E. Tlelo-Cuautle, I. Cruz-Vega, “Enhanced FPGA implementation of Echo State Networks for chaotic time series prediction,” Integration, Vol. 92, pp. 48-57, Sep. 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vlsi.2023.05.002
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Revista Mexicana de Ingenieria Biomedica

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Upon acceptance of an article in the RMIB, corresponding authors will be asked to fulfill and sign the copyright and the journal publishing agreement, which will allow the RMIB authorization to publish this document in any media without limitations and without any cost. Authors may reuse parts of the paper in other documents and reproduce part or all of it for their personal use as long as a bibliographic reference is made to the RMIB. However written permission of the Publisher is required for resale or distribution outside the corresponding author institution and for all other derivative works, including compilations and translations.







